By now energy-efficient lighting is hardly a new concept. You’ve likely heard of energy-saving bulbs, seen them in someone’s home, and maybe even tried buying some. However, energy-efficient lighting has come a very long way in recent years. Gone are the days of odd-looking bulbs, turning on the lights and having to wait a couple of minutes before you can see anything, or getting home only to find out that the lightbulb you bought is cold and blue, rather than the warm inviting color most of us are used to.
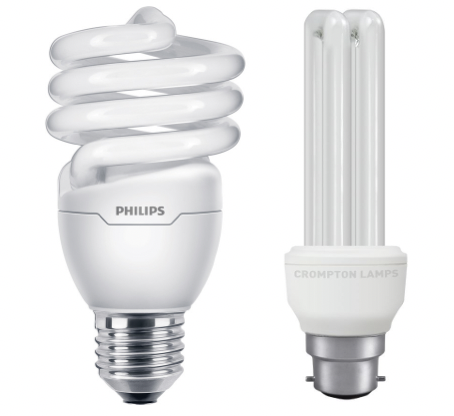
This is all thanks to recent innovations in LED technology. To understand energy-saving light bulbs, it’s important to go back to the source. Over a decade ago, the first energy-saving light bulbs to hit the market and become commonplace were CFL bulbs or Compact Fluorescent Lights. You may recognize CFL bulbs because of their odd, twisted shapes. CFL bulbs are essentially the long fluorescent light bulbs like you typically find in offices and classrooms, twisted around to fit in the space of a normal light bulb. While this certainly was an innovation in lighting, many years ago, the main drawbacks people found with these bulbs were the harsh blue-white light they emit and having to wait several minutes for them to warm up.
What are LED’s?
Enter LED bulbs. We all know LED’s as the small “light-emitting diodes” that power our television remotes, and other small electronics’ lights. LED’s are known for their low energy consumption, high, sometimes laser-like light output, and their ability to work for hours without overheating. While LED’s were initially limited to cold, white light, in recent years LED’s have taken the home lighting industry by storm. LED’s now outpace traditional bulbs in almost every sense of the word. They are dimmable, shatterproof, come in an array of colors and temperatures, and are extremely long-lasting. A single LED bulb on average can save around $35 on electricity versus a traditional incandescent or halogen light bulb over the course of a year. When scaling this up and replacing all of the lightbulbs in your home, the energy savings become exponential. LED bulbs tend to last 10 to 25 times longer, meaning that they will likely last you a decade or longer. While LED’s tend to cost slightly more than a normal incandescent bulb, the savings, and the hassle of not having to constantly replace them definitely outweigh the cost. They are also an easy way to reduce your carbon footprint. If you are unfamiliar with your personal carbon footprint, a good first step is to start by understanding its size. You can use this online calculator from the EPA to give you an idea.
Are LED’s all Blue or White?
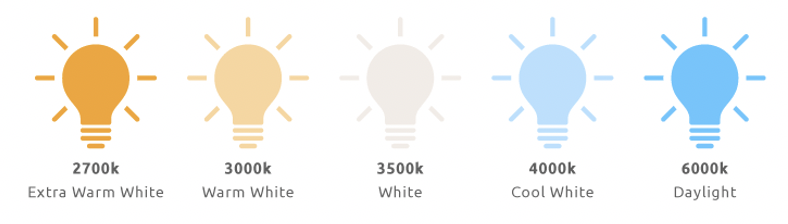
One thing that is very important when choosing an LED bulb is to look at the light color the bulb emits. In America, we are used to having our homes lighted by warm light such as what a traditional incandescent bulb emits. While warm light is very nice for living areas, sometimes white light can be useful, such as in bathrooms or office areas where more light may be needed. Below you will find a simple guide to choosing warm and cool light bulbs. Light color is measured in Kelvins.
Most bulbs apart from having the temperature listed in kelvins will also have the color listed on the box.

Color descriptions are not universal, however, you will notice that the bulbs come in “cool”, “daylight” or “white light”, and then warm light, which is also often referred to as “soft white”.
Next time you take a trip to your local hardware or big box store, it is worth a visit to pass by the lighting aisle and familiarize yourself with the bulbs that are offered. LED’s are here to stay and are certainly the lighting choice of the future. They offer affordable, long-lasting, dynamic lighting that is good for your pocket and good for the environment. It is safe to say that because of these factors switching to energy-saving lighting is a “no-brainer”. You can find out more information on energy-saving bulbs at EnergyStar.gov.
Thank you to guest author Allen Shuford, a renewable energy advisor at Theswitch.co.uk

Leave a Reply