Climate science
-

Measurements of sea level across the world show rising waters along most ocean coastlines, including the United States. But according to a story by WRLN in Miami, the regular forecasts for high and low tide do not take that rising water into account yet, leading to bigger errors in tide forecasts than would normally be…
-

Every fall, deciduous trees in the Southeast (and elsewhere in the country) change color. Every year, we get asked why. The North Carolina Climate Office has a good description at https://climate.ncsu.edu/climateblog?id=302&h=5666e5c1. Will this year’s drought impact the leaf color in the Southeast? WSB addresses that in a recent article here.
-

A flash drought is a severe drought which comes on suddenly, usually through the combination of a near total lack of rainfall and much warmer than normal temperatures. We are seeing a flash drought in the Southeast now, and conditions are rapidly worsening because of the July-like weather. Flash droughts are hard to predict and…
-

Historical records of hurricanes only go back a few hundred years and are captured mainly in places where people lived in coastal areas. How do climatologists learn about hurricanes which occurred before humans were there to record their occurrence? It turns out that hurricanes leave recognizable patterns of mud and sand deposits in coastal areas…
-

If you think the weather in the Southeast this year has been bad, compare how life in Jacobabad, Pakistan is. This is known as one of the hottest cities on Earth, and could provide a taste of what life could be like for more of the world in the future if global warming continues. You…
-
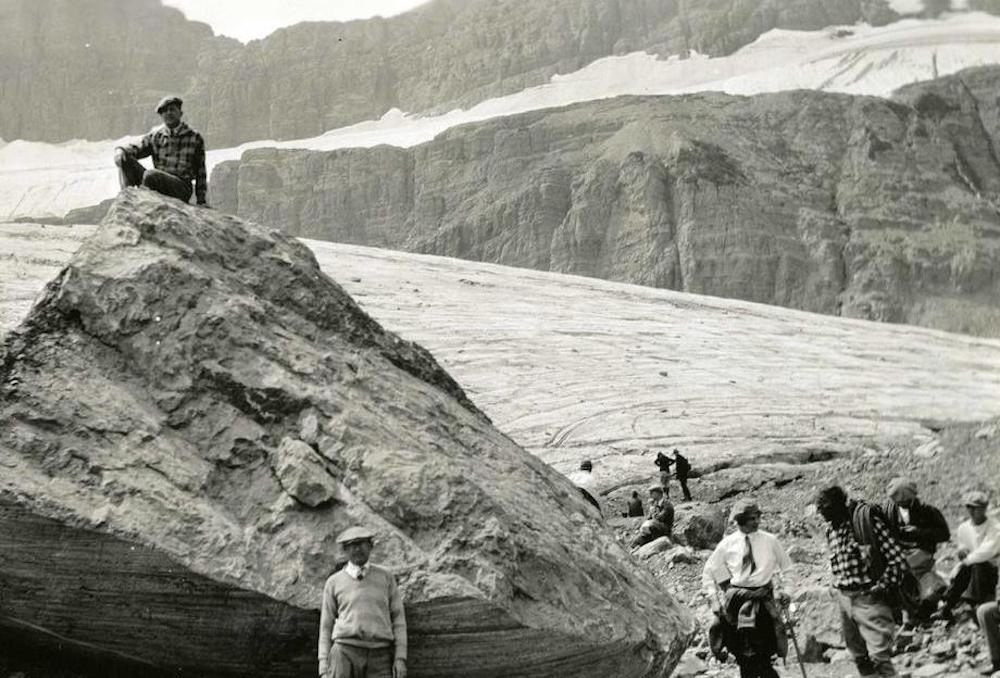

I love Atlas Obscura for its highlighting of quirky places and foods. They provide a look at some seldom-seen local sites, and provide a historical context for why these sites exist. A year ago this week AO published a story that show many before and after pictures of glaciers in national parks showing how they…
-
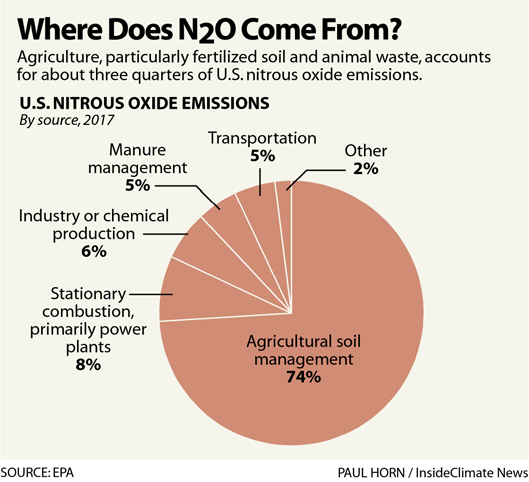
If I asked you to list some greenhouse gases, you would probably start by listing carbon dioxide and then perhaps methane. But for agriculture, nitrous oxide is arguably more important, because many sources of nitrous oxide are from farming, for example from microbes in fertilized soil or animal manure. And nitrous oxide has 300 times…