-
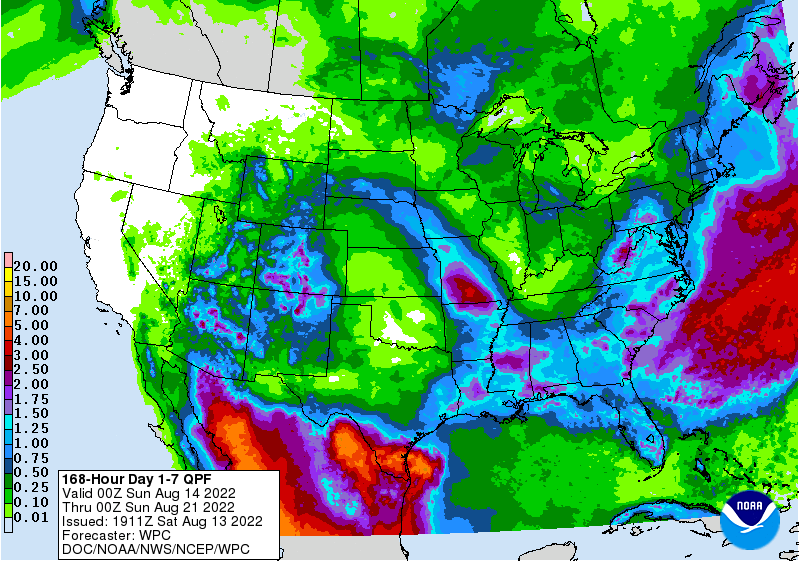
The latest 7-day QPF map shows that most areas within the region should receive some rain this week. In most cases, they are predicting 0.5 to 1.5 inches. Slightly heavier amounts in eastern North Carolina and along the coast with the possible spin-up of a low along the old stationary front that could enhance the…
Posted in: Climate outlooks -

One of the ways that producers might be able to adapt to the changing climate is by producing new crop varieties that are more resistant to drought, since drought is expected to increase in the future as temperatures get warmer and evaporation and evapotranspiration increase. Plant breeders are looking for plants that have characteristics that…
-
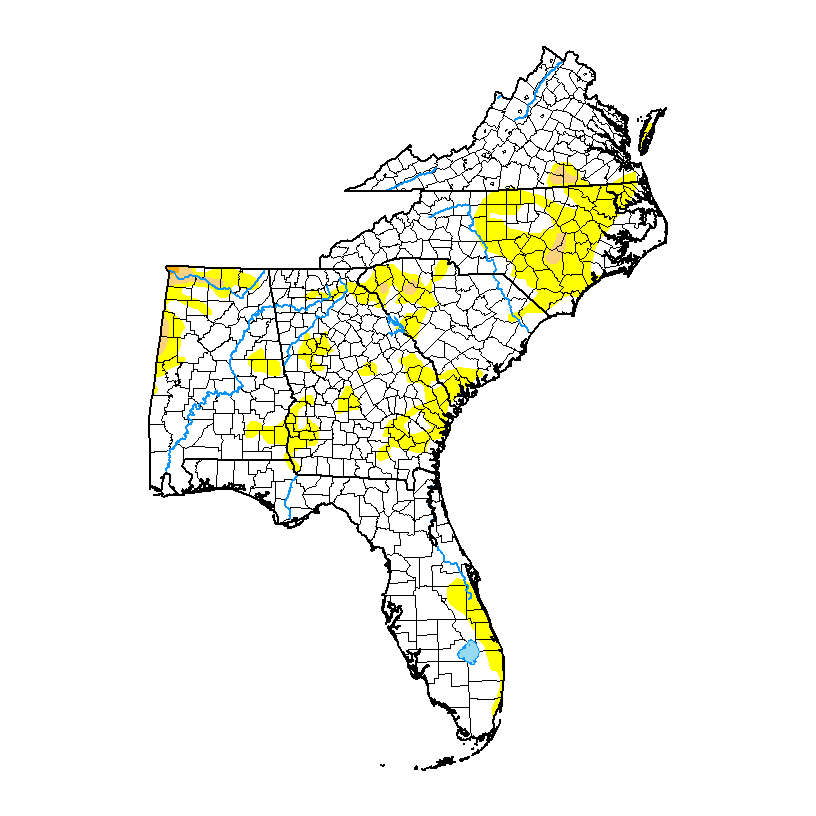
The latest Drought Monitor, released today, shows that almost all of the drought in the region has improved to lingering abnormally dry conditions. There are still a few small patches of drought in North Carolina and Alabama. Conditions in Puerto Rico have also improved, although some drought remains there as well. Most of the region…
Posted in: Drought -
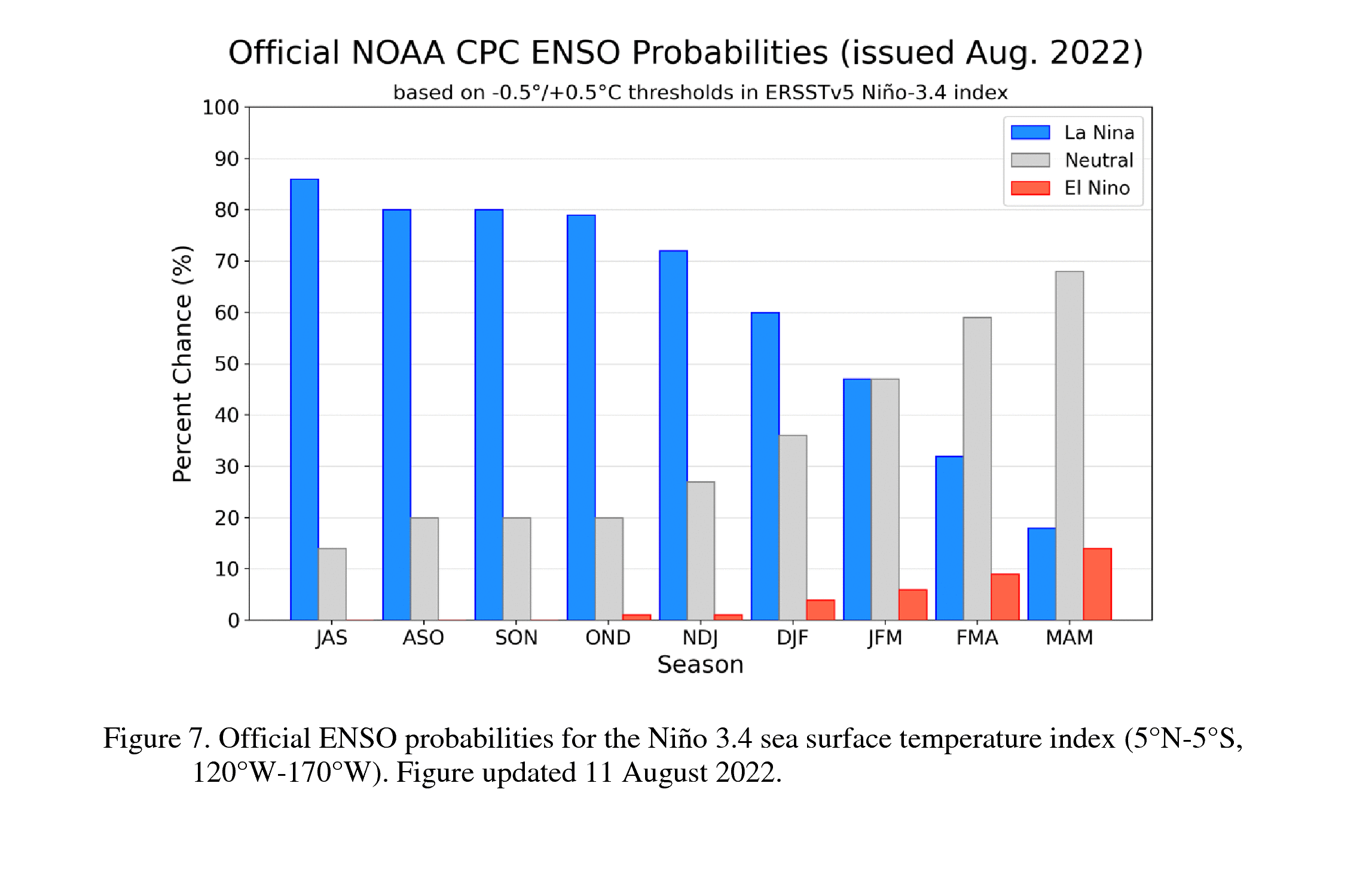
The latest El Nino discussion was released today. It shows that there is a strong likelihood that La Nina will continue through 2022, with a return to neutral conditions likely by spring. You can read more at their summary page. That means that even though the tropics are quiet now, we expect them to ramp…
-
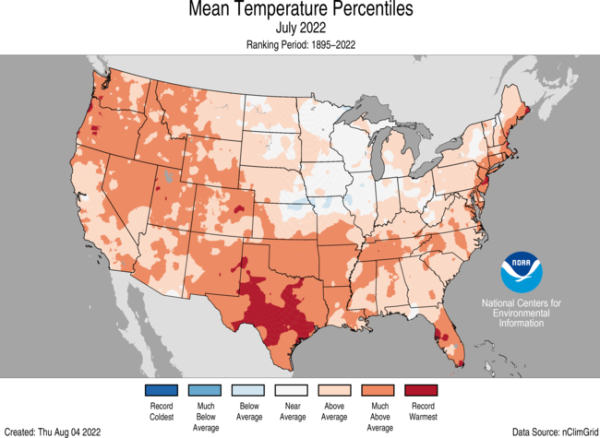
NOAA released the latest monthly summary for the United States for July 2022 earlier this week. It shows that this was the third warmest July in 128 years of record. In the Southeast, areas of central Florida experienced their hottest July on record. Rainfall varied quite a bit across the country and overall ranked in…
Posted in: Climate summaries -

While most farmers this year have been grateful for the transition to a rainier pattern after a dry June, it has caused some problems for farmers. Hot temperatures and saturated soils meant an early end to pollination and the early end of the squash and cucumber seasons. The wet soil also hindered harvest of some…
-

I am speaking at a workshop this week in Atlanta that looks at drought prediction and impacts in the Southeast. One of the main topics of the workshop is flash drought, a drought that rapidly intensifies as rainfall drops to near zero in a prolonged dry spell and temperatures rise well above average. If you…