-
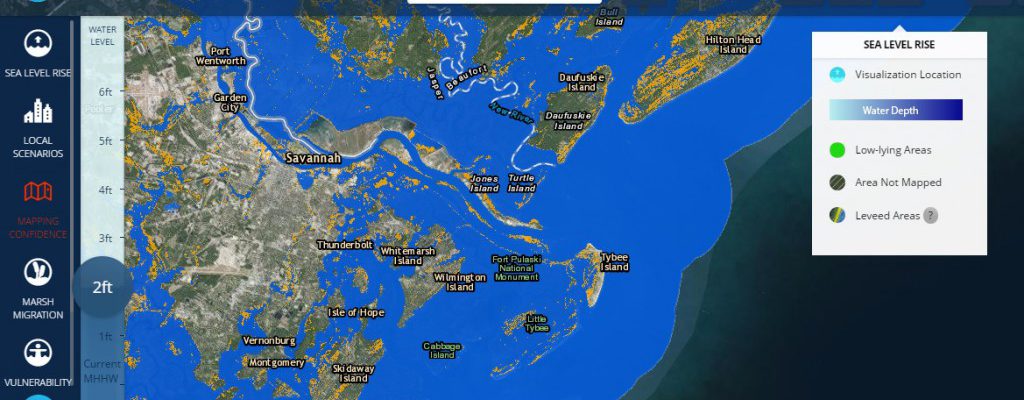
Here are a couple of different tools I’ve run across this week which look at the effects of rising sea levels on coastal areas of the US. The Tides and Currents site at https://tidesandcurrents.noaa.gov/sltrends/sltrends.html shows how local sea level rise differs from global sea level rise. The total sea level rise is a combination of rising…
-

The Vegetable and Specialty Crop News posted a story this week about the development of tea as a new specialty crop in the Southeast. Of course there have been some tea plantations in the South in the past, but a Florida researcher is looking into adding tea to the bouquet of specialty crops growing in…
-
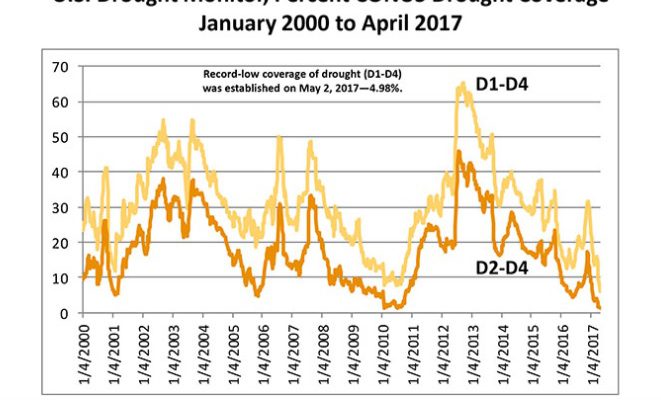
USDA meteorology Brad Rippey provides a look at summer weather across the US in an article published this week at Growing Georgia here. While drought across the nation is at very low levels, the drought in the Southeast looks like it could continue at least on the short term, although he is hopeful that once…
Posted in: Climate outlooks -

NASA released their monthly global climate summary for April 2017 today. It shows that April was the second warmest in 137 years of record following the record setting year in 2016. While most areas of the globe were above normal, especially in the Arctic, you can still find some regions that were below the long-term…
Posted in: Climate summaries -

Just in case you did not know, the World Meteorological Organization has a five-minute video explaining everything that meteorologists do using cute hand drawings. Did you know that the broadcast meteorologists you see on television are actually just a small proportion of all of the meteorologists working for government, private industry, and in the military?…
Posted in: Interesting weather images -

Have you ever heard the comment that in the 1970s climate scientists were talking about global cooling? I get this statement frequently when I give talks to the public. And yet, this was proven false a decade ago. This article from the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society (which popped up in my Facebook feed…
-
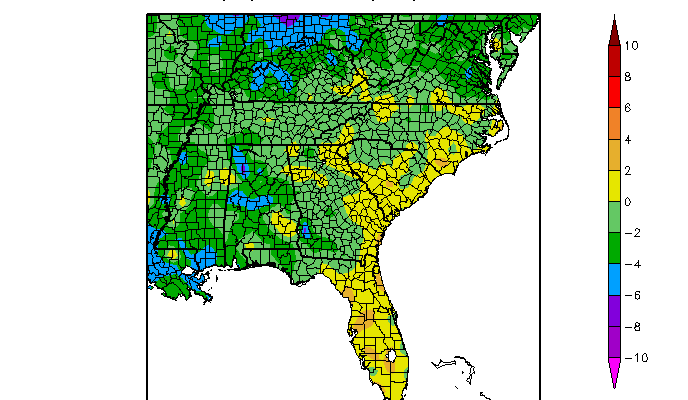
At halfway through the month, the preliminary climate statistics maps from the High Plains Regional Climate Center show that temperatures in many parts of the region are running a little below normal. If this continues, Georgia will see its first below-normal month since January 2016. But with temperatures expected to be above-normal this week, we…
Posted in: Climate summaries