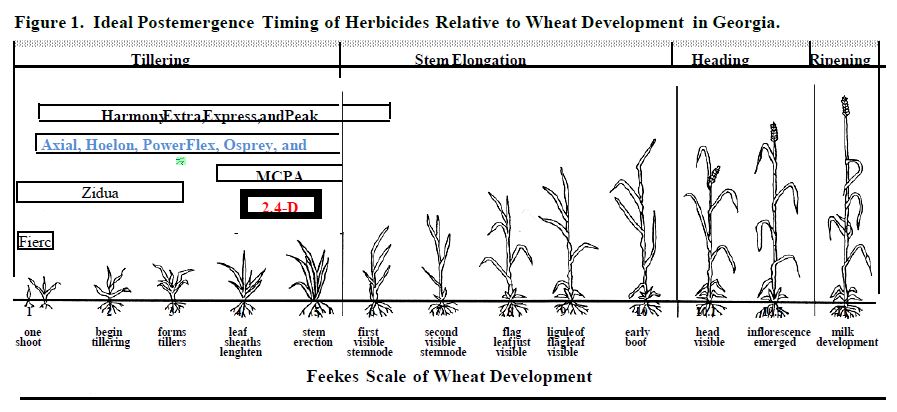
We don’t have as much small grain planted this year, but wanted to update the weed control nonetheless. With our small grains planted for grain or seed, and considering a normal planting, we need to get our weed control done by Christmas. Once we get to February, it’ll be too late to manage ryegrass and wild raddish with herbicides.
BROADLEAF WEEDS
Our broadleaf program is mostly based around wild radish. Radish seedpods can contaminated our harvested grain. Because they are similar in size and shape to our planted to wheat, it’s hard to clean them.Use of Harmony for broadleafs has a large window for safe application, but do not apply 2,4-D to small grain that is not fully tillered. Also, do not apply 2,4-D after small grain is jointing.
Below is a list of most effective wheat program from Dr. Stanley Culpepper:
- Harmony TS followed by MCPA or 2,4-D*
- Harmony TS + MCPA or 2,4-D**
- 2,4-D alone
- Harmony Extra alone
If you have early emerging small grain with weeds, the first program is your only option. If you have later emergence, and few emerged weeds, you can go with the second program. Keep in mind, we need to be above 50 degrees when treating. The sooner you apply before cold weather the better.
* If we are not at full tiller, MCPA is what we need to use. If you are not sure if you are at full tiller, use MCPA; Also, 2,4-D is more effective on larger weeds.
** You may try a new broadleaf herbicide for wheat, barley, and triticale called QUELEX. We can apply from 2-leaf to flag leaf, which is a much wider window of application compared to 2,4-D and even MCPA. We have limited research, but so far shows similar radish (<8″) control compared to 2,3-D with LESS crop injury potential. 2,4-D may be more effective on larger radish.
ITALIAN RYEGRASS

Italian Ryegrass popping up in Wrens Abruzzi rye
In terms of genetic stability, ryegrass is worse than pigweed. For control of ryegrass, it is important that each field is treated only once every two years with the respected chemistry. For instance, if we use Axial this year, we do not spray Axial or Hoelon on that piece of ground next year at all. The same applies to Powerflex and Osprey. If we do not rotate, we will lose the chemistry. Below is a graph of these chemical classes:
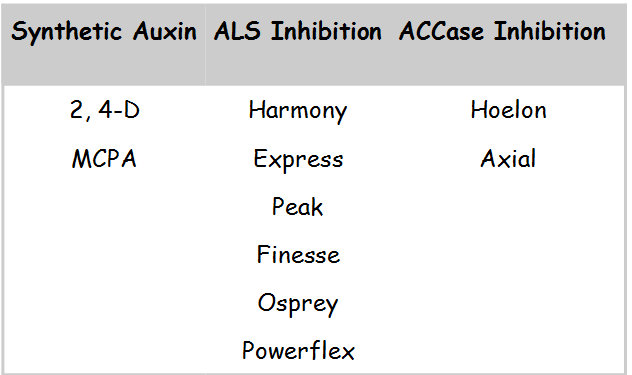
What if we have resistance to one of these four? Dr. Culpepper advises to get out of that field completely for 3 – 5 years.
Growth Stage
What is full tiller? Following emergence and the spike stage, small grain crops begin to tiller. These are essentially stems that will produce a grain head in the future. When we have 5 or 6 tillers on a plant, it is considered full tiller. Depending on growing degree days, it will generally take between 20 and 35 days to reach full tiller. With the same herbicides, we don’t want to treat once crop enters the jointing stage. Just before jointing, the stems will elongate. At the base of the stem, you will feel a swelling of the stem (almost like a bee bee inside the stem) which is the first node or joint. The joint is the growing point. The plants have now moved into the reproductive growth stages.